The 5 C’s according to Fairy Tale Diamond
In order to get the perfect diamond for your diamond engagement ring there are several factors to consider. These all determine the value and quality of a diamond. These are well known as the 4c’s of a diamond and the combination of all these make it possible to evaluate the diamond.
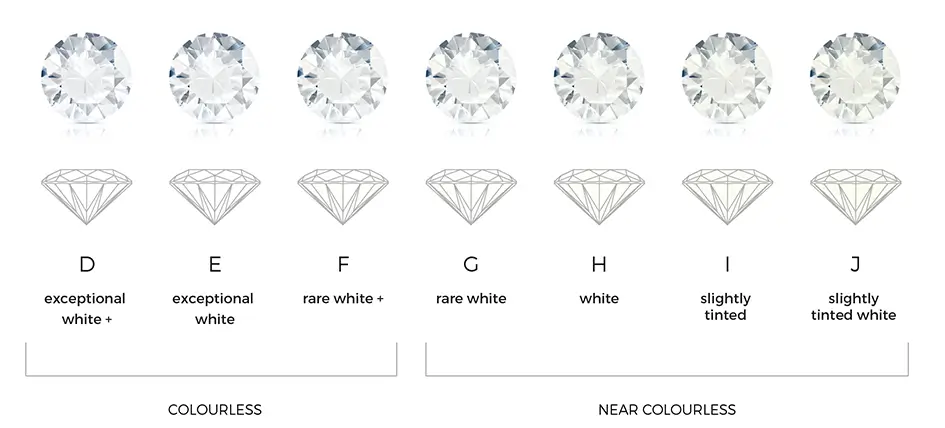
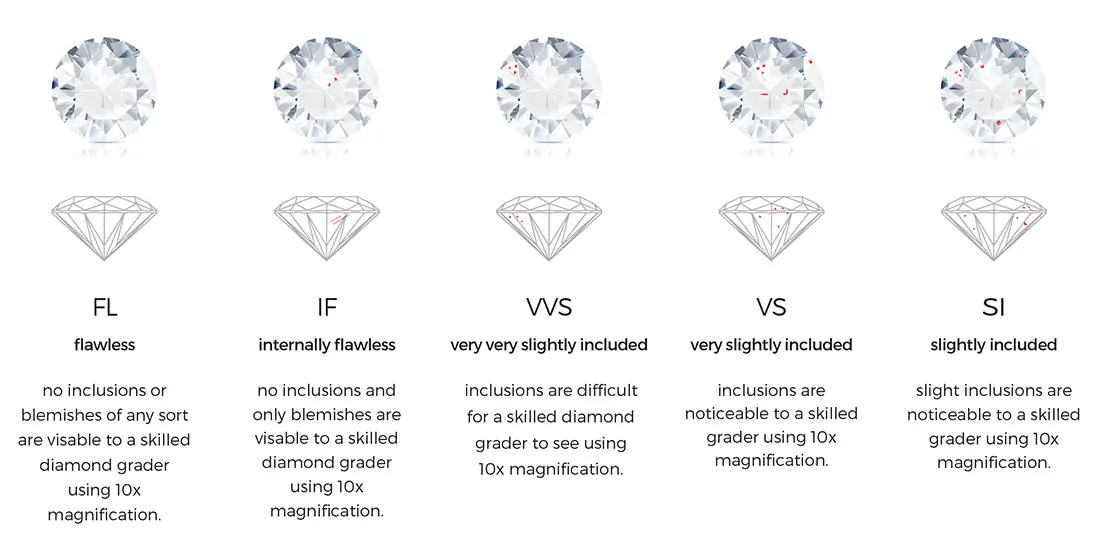
The 4c’s are: Colour, Clarity, Cut and Carat
At Fairy Tale Diamond we look at the 5c’s, where the 5th C is the certificate.
We also look at the major difference between Lab Grown and Natural diamonds
Cut
The cut grading currently only applies to Round diamonds as they are technically easier to measure in terms of light performance. Other shapes – such as Princess cuts, Cushions cuts, Emerald shapes, do not have a cut grading on their certificate but 77 Diamonds provide an estimated cut grading based on equivalent parameters.
Cut grades range from Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair and Poor. The grading takes into account various attributes of the diamond that cannot be seen or measured with the untrained eye. An excellent cut grading will have the best light performance, mainly influenced by the relationship of surface table and the depth of the diamond (not too deep or too shallow).
A well cut diamond can make light perform in breath-taking ways, which results in magnificence of the diamond itself, displaying 3 important attributes:
1. Brilliance – the total light reflected from a diamond
2. Fire – the dispersion of light into the colours of the spectrum
3. Scintillation – the sparkle when a diamond is moved
The factors which determine a diamonds overall cut is table size, crown angle and pavilion as well as the thickness of the girdle.
On a certificate only a Round Diamond will get a cut Grade.
Hearts and Arrows:
These are mostly round diamonds with superior cutting quality. Hearts and arrows are highly symmetrical, reflected light patterns which visually demonstrate the optimal symmetry of an excellent cut diamond. The name refers to 2 separate light patterns seen when a diamond is viewed through the pavilion (face down) or the table (face up).
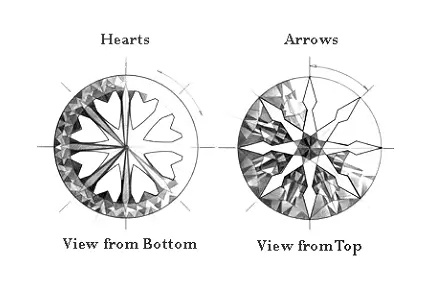
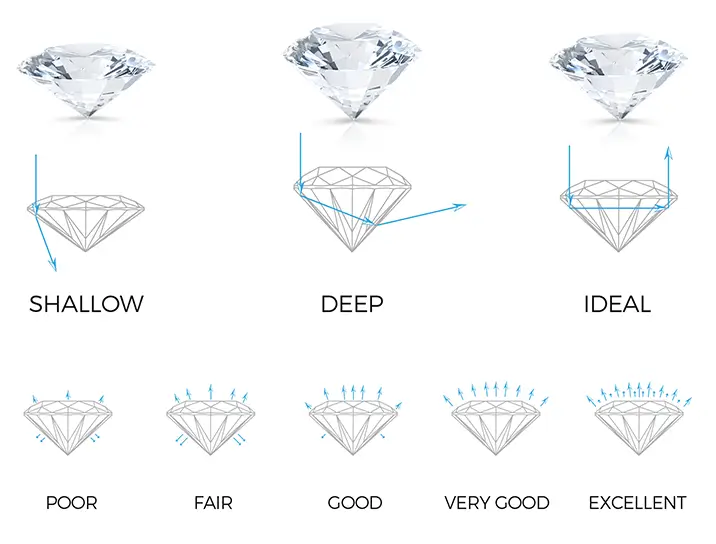
The Reflective Qualities of A Diamond Cut:
When a diamond is perfectly cut, light rays from all sides are bent towards the centre of the stone and reflected back though the top in a rainbow of light. If a diamond is not perfectly cut, light will escape through the base or sides of a diamond as seen in the images below:
A diamond certificate is the evaluation by a third-party, not by either the diamond buyer or seller. Unfortunately, a 3rd party certification is necessary, as it would be easy for an unscrupulous jeweller to take advantage of an uninformed buyer and sell him or her a stone, which ostensibly has much better characteristics than it really does. There are a number of ways unsuspecting buyers might land a bad deal. If the diamond is not certified, there is a good chance you may be buying a stone that is one or more grades below stated values in terms of carat weight, colour, clarity, or cut. Without a certificate, issued by a reputable agency, such as GIA or IGI, a buyer relies on a jeweller’s integrity that the diamond’s 4C characteristics are accurate and not overstated.
Conflict Free Diamonds
Fairy Tale Diamond uses only conflict-free diamonds which are obtained from legitimate diamond sources that have been certified through the worldwide recognized Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS).
Fairy Tale Diamond will not knowingly use conflict diamonds and adhere to the Kimberly process which was organised to stem the flow of conflict diamonds in Africa.
A blood diamond (also called a conflict diamond, converted diamond, hot diamond, or war diamond) is a term used for a diamond mined in a war zone and sold to finance an insurgency, an invading army’s war efforts, or a warlord‘s activity. The term is used to highlight the negative consequences of the diamond trade in certain areas, or to label an individual diamond as having come from such an area. Diamonds mined during the recent civil wars in Angola, Cote d’Ivoire, Sierra Leone, and other nations have been given the label.
For more information visit http://www.kimberleyprocess.com/